| .. | ||
| architecture.png | ||
| README.md | ||
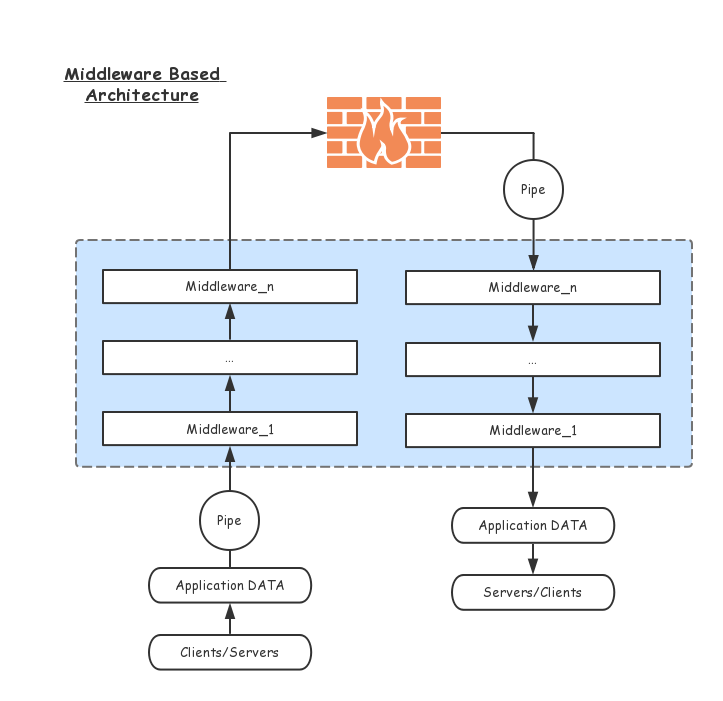
Architecture
Proxy Application Data
To take over data send and receive of applications, we must find a widely used proxy protocol. Http/Socks5/Socks4/Socks4a are ideal, they only work on the client side, so don't worry about being attacked.
References
Pipe
Pipe is a duplex facility for dealing with data streaming. A pipe is created once a connection was open.
Pipe puts all middlewares in cascade(both upstream and downstream), feeds original data to the first middleware from time to time and gathers processed data from the last layer of all middlewares.
Middleware
Middleware is a director which used for processing input data to output data from/to other middlewares.
Similar to TCP/IP, you can define your own protocol in each layer. Application data are processed step by step from the lowest layer to the top. Middlewares here act as specific layers in the stack.
Here is the original shadowsocks protocol implemented in blinksocks using the following config:
{
...
"presets": [
{"name": "ss-base", "params": {}},
{"name": "ss-stream-cipher", "params": {"method": "aes-256-cfb"}}
]
...
}
These two presets act as two middlewares, processing data from the bottom to the top.
+--------+----------------------------------------+
| IV | PAYLOAD |
+--------+----------------------------------------+ <-------+
| 16 | Variable | |
+--------+----------------------------------------+ |
|
{"name": "ss-stream-cipher", "params": {"method": "aes-256-cfb"}}
|
+------+----------+----------+-----------+ |
| ATYP | DST.ADDR | DST.PORT | PAYLOAD | |
+------+----------+----------+-----------+ <-------+
| 1 | Variable | 2 | Variable | |
+------+----------+----------+-----------+ |
|
{"name": "ss-base", "params": {}}
|
+-----------+ |
| DATA | |
Application Data -----> +-----------+ --------+
| Variable |
+-----------+
Ordinarily, DST.ADDR and DST.PORT is required to be sent to server(like "ss-base" preset),
otherwise server cannot figure out where to send data to.
The framework will prepend proxy preset to the preset list on client side. Action(PROXY_HANDSHAKE_DONE) is fired
once this preset resolved the target address. Other presets(such as "ss-base") who want to use the address should implement
onNotified(action) method, the address is stored in action.payload.targetAddress.
// core/socket.js
let presets = __PRESETS__;
// prepend "proxy" preset to the top of presets on client side
if (__IS_CLIENT__ && presets[0].name !== 'proxy') {
presets = [{name: 'proxy'}].concat(presets);
}
// create middlewares and pipe
const middlewares = presets.map((preset) => createMiddleware(preset.name, preset.params || {}));
Store target address for further use:
// presets/ss-base.js
import {IPreset} from './defs';
export default class SsBasePreset extends IPreset {
_atyp = ATYP_V4;
_host = null; // buffer
_port = null; // buffer
onNotified(action) {
if (__IS_CLIENT__ && action.type === PROXY_HANDSHAKE_DONE) {
const {type, host, port} = action.payload.targetAddress;
this._atyp = type;
this._port = numberToBuffer(port);
this._host = type === ATYP_DOMAIN ? Buffer.from(host) : ip.toBuffer(host);
}
}
// ...
}
Preset
Preset is the implementation of middleware, for examples you can check out src/presets, there are several built-in presets already.
Custom Preset
A typical preset should extends IPreset interface:
// custom.js
import {IPreset} from './defs';
export default class CustomPreset extends IPreset {
clientOut({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
// next(buffer); async
return buffer; // sync
}
serverIn({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
return buffer;
}
serverOut({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
return buffer;
}
clientIn({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
return buffer;
}
}
| METHODS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clientOut | client received data from application, and ready to forward data to server |
| serverIn | server received data from client, and ready to forward data to real destination |
| serverOut | server received data from real destination, and ready to backward data to client |
| clientIn | client received data from server, and ready to backward data to application |
NOTE:
server*are used on the server side whileclient*are used on the client side.
Every method gets an object which contains three parameters you need:
| PARAM | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| buffer | output from the previous preset |
| next(buffer, isReverse) | asynchronously process buffer to the next preset, if isReverse is true, then send data back to the previous preset |
| broadcast(action) | broadcast an action to other middlewares |
| direct(buffer, isReverse) | ignore the following presets, send data directly to fsocket or bsocket |
| fail(message) | report that the preset is fail to process |
Presets Decoupling
There may be coupling between presets, you can pass an action to broadcast().
Action is a plain object which only requires a type field:
// action
{
type: <string>,
...
}
Once broadcast, all other middlewares will receive the action in onNotified(action) immediately:
// custom.js
import {IPreset} from './defs';
export default class CustomPreset extends IPreset {
/**
* how to deal with the action, return false to ignore
* @returns {boolean}
*/
onNotified(/* action */) {
return false;
}
// ...
}
NOTE: onNotified is synchronous.
Hooks
There are two hooks available:
// custom.js
import {IPreset} from './defs';
export default class CustomPreset extends IPreset {
beforeOut({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
return buffer;
}
beforeIn({buffer/* , next, broadcast, direct, fail */}) {
return buffer;
}
// ...
}
| METHODS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| beforeOut | pre-process before *Out() |
| beforeIn | pre-process before *In() |
Access User Configuration
You can access user configuration from your preset:
import {IPreset} from './defs';
export default class CustomPreset extends IPreset {
constructor() {
super();
console.log(__KEY__);
}
}
available constants
| NAME |
|---|
| __ALL_CONFIG__ |
| __IS_SERVER__ |
| __IS_CLIENT__ |
| __LOCAL_HOST__ |
| __LOCAL_PORT__ |
| __TRANSPORT__ |
| __SERVER_HOST__ |
| __SERVER_PORT__ |
| __SERVERS__ |
| __KEY__ |
| __PRESETS__ |
| __DNS__ |
| __DNS_EXPIRE__ |
| __TLS_CERT__ |
| __TLS_KEY__ |
| __TIMEOUT__ |
| __REDIRECT__ |
| __LOG_PATH__ |
| __LOG_LEVEL__ |
| __WORKERS__ |